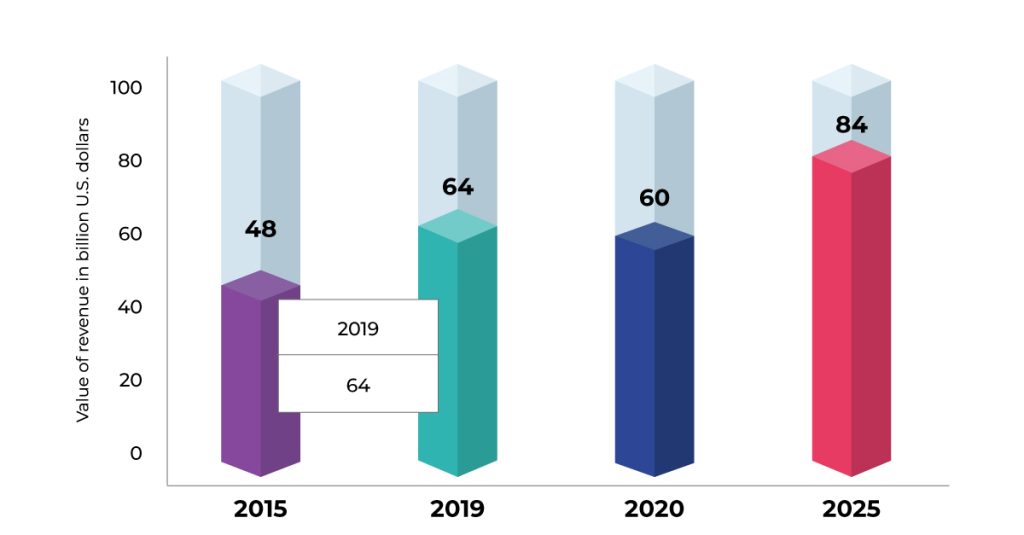
Payment revenue in the Middle East was at $60 billion USD in 2020. This number is predicted to have at least a 30% hike by the year 2025. Which means by 2025 the payment revenue in the middle east is set to reach $84 billion USD. That’s an above average compound annual growth rate of 7%. If that happened, then it is outpacing regional GDP growth estimates.
In the coming years, major payment and messaging platforms will focus on upgrading their systems to help financial institutions deliver better digital services, streamline operations, enhance compliance measures, and achieve nearly real-time execution. Many of these platforms are moving to ISO 20022 messaging standards for high-value and cross-border payments to meet these goals.
ISO 20022 in Payment industry, what to expect?
The Middle East is at the forefront of payment innovation, and ISO 20022 is rapidly transforming the financial industry in the region. As banks and financial institutions adapt to these changes, understanding the potential of ISO 20022 becomes essential for leveraging its full benefits. Here’s an overview of how the Middle East is embracing payment modernization and addressing challenges while unlocking new opportunities with ISO 20022.
Current State of ISO 20022 in the Middle East
ISO 20022 has been making waves in the financial sector, particularly in the Middle East. Banks in the region are juggling multiple modernization projects to align with ISO 20022 for both domestic and cross-border payments. Initiatives like SWIFT, GCC RTGS, BUNA, and instant payment schemes are reshaping the payment landscape.
Saudi Arabia is taking significant strides under its Vision 2030 initiative, aiming to achieve 70% non-cash transactions by 2030. The UAE is also advancing with its National Payment Systems Strategy, introducing a National Instant Payment Platform that allows real-time funds transfers around the clock. These advancements highlight the region’s commitment to enhancing its payment ecosystem.
Challenges in Providing Advanced Payment Services
Despite the progress, banks in the Middle East face significant hurdles. Tighter liquidity, growing competition, and a demanding macroeconomic environment add pressure to their operations. Balancing day-to-day business with the need to upgrade technology is no small feat.
Legacy systems often hinder progress, making it difficult to achieve faster, more streamlined processes. Financial institutions must carefully manage their resources to keep pace with client needs while staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Maximizing ISO 20022 Benefits
To unlock the full potential of ISO 20022, financial institutions must go beyond basic format changes and fully utilize its rich data capabilities. Here are some strategies to maximize the benefits:
Transitioning Beyond “Like for Like”: Many banks initially focus on translating legacy formats into ISO 20022. However, real benefits come from leveraging the enhanced data features of the standard. By 2025, market infrastructures like the Bank of England will mandate structured data, including purpose codes for CHAPS payments and Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs) for transactions. Embracing these features will enable institutions to streamline processes and improve compliance.
Automating Payment Reconciliation with Structured Remittance: Structured remittance information can significantly reduce manual errors and resource costs in B2B transactions. By including essential data like invoice numbers and expanding to detailed information, banks can automate reconciliation processes. Following remittance data tiers provides a framework for adopting these enhancements.
Smart Internal Routing Using Enhanced ISO 20022 Codes: The new ISO 20022 codes improve internal payment routing. Service-level codes help direct payments to the right processing engine, optimizing efficiency across regions and payment types. Mandated purpose codes for specific transactions also enhance payment prioritization and product development.
Mitigating Fraud Risk with LEI: To combat fraud, the Bank of England requires LEIs for transactions between UK banks. This approach may inspire similar mandates in other regions. Precise party identification through LEIs and BIC codes reduces delays in sanctions screening and improves straight-through processing rates. Adopting hybrid models for capturing and verifying LEIs can further streamline this process.
Stay Relevant in a highly Competitive Market: To thrive in a highly competitive environment, Middle Eastern banks need cutting-edge technology. Advanced, low-code platforms with microservices, real-time capabilities, and API integration offer the flexibility required to meet regulatory demands and customer expectations. Cloud technology, particularly PaaS models, brings opportunities for improved data analytics, cost efficiency, and operational flexibility.
Modernizing payment infrastructures and collaborating with innovative payment providers are crucial for building a digital payments ecosystem. This approach will help the Middle East achieve significant digital transformation, aligning with global trends while addressing regional challenges.
By understanding and applying the capabilities of ISO 20022, financial institutions in the Middle East can not only keep up with industry changes but also position themselves as leaders in payment innovation.
- Unlocking the Potential of AI in Payment Solutions - March 25, 2025
- How to leverage Payment Innovation of the Middle East with ISO 20022 - December 26, 2024
- How Artificial Intelligence in Banking Transforms Customer Experience - December 9, 2024

 Write to Us
Write to Us